

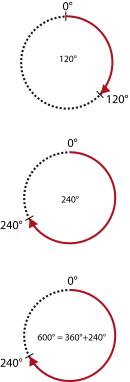
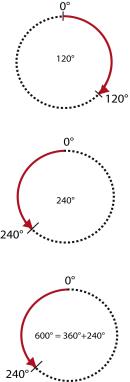
An absolute target position is always approached by the shortest path. Relative movements are not executed "path-optimized".
| Position range | Effect |
|---|---|
|
Target position < circumference (Example 120° < 360°) |
The drive moves to the target position within 360°. |
|
Target position = circumference (Example 120° = 120°) |
The drive remains in position. |
|
Target position > circumference (Example 600° -360° = 240°) |
The drive moves to the position within the circumference (target position - (n x circumferential length)) |
Tabelle: Path-optimized movement
Graphic for indexing table with/without path optimization
| Not path-optimized | Path-optimized |
|---|---|
|
|
Bild: Path optimization
Copyright © LTi DRiVES GmbH, Januar 2013, ID-Nr.: 0842.26B.1-00 DE